代码随想录刷题记录 Day2
To Do List
- DAY 1 回顾
- LeetCode 977. 有序数组的平方 / Squares of a Sorted Array
- 滑动窗口基础
- LeetCode 209. 长度最小的子数组 / Minimum Size Subarray Sum
- 209 题扩展题目
- 再提循环不变量:LeetCode 59. 螺旋矩阵 II / Spiral Matrix II
- 59 题扩展题目
- 总结 / Summary
1. DAY 1 回顾
Day 1 学习内容:Link
- 认识了数组的基本结构和增删查改操作。
- 学习了二分法以及双指针法
- 一刷 LeetCode 6 题 Link
2. LeetCode 977. 有序数组的平方 / Squares of a Sorted Array
难度:简单
题目要求:
(CN)
给你一个按 非递减顺序 排序的整数数组 nums,返回 每个数字的平方 组成的新数组,要求也按 非递减顺序 排序。
- 请你设计时间复杂度为
O(n)的算法解决本问题
(EN)
Given an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing order, return an array of the squares of each number sorted in non-decreasing order.
Squaring each element and sorting the new array is very trivial, could you find an O(n) solution using a different approach?
Example 1:
1 | Input: nums = [-4,-1,0,3,10] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: nums = [-7,-3,2,3,11] |
Constraints / 提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^4-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4numsis sorted in non-decreasing order. (nums已按 非递减顺序 排序)
与之前的数组不同的是,这道题当中数组包含了负数,而负数的平方为正数,要想平方后排序,需要用到两个快指针 fs 和 fe,分别指向数组的 0 位置和 nums.size - 1 位置 ,慢指针 s 则指向一个新数组的 nums.size - 1 位置,从右向左移动指针,记录平方后的元素;快指针则需要对平方后的元素进行比较:
1 | 1 若 (nums[fs])^2 > (nums[fe])^2,则将 nums[fs] 赋给 s,fs 向右移动一位,s 向左移动一位 |
解法:
Java:
(For Leetcode / IDEA Custom)
1 | class Solution { |
JavaScript:
(For Leetcode / WebStorm Custom)
1 | /** |
3. 滑动窗口基础
4. LeetCode 209. 长度最小的子数组 / Minimum Size Subarray Sum
难度:中等
题目要求:
(CN)
给定一个含有 n 个正整数的数组和一个正整数 target 。
找出该数组中满足其和 ≥ target 的长度最小的 连续子数组 [nums(l), nums(l+1), …, nums(r-1), nums(r)] ,并返回其长度。如果不存在符合条件的子数组,返回 0.
- 如果你已经实现
O(n)时间复杂度的解法, 请尝试设计一个O(n log(n))时间复杂度的解法。
(EN)
Given an array of positive integers nums and a positive integer target, return the minimal length of a subarray whose sum is greater than or equal to target. If there is no such subarray, return 0 instead.
If you have figured out the O(n) solution, try coding another solution of which the time complexity is O(n log(n)).
Example 1:
1 | Input: target = 7, nums = [2,3,1,2,4,3] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: target = 4, nums = [1,4,4] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: target = 11, nums = [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1] |
Constraints / 提示:
1 <= target <= 10^91 <= nums.length <= 10^51 <= nums[i] <= 10^4
解法:
5. 209 题扩展题目
6. 再提循环不变量:LeetCode 59. 螺旋矩阵 II / Spiral Matrix II
难度:中等
题目要求:
(CN)
给你一个正整数 n ,生成一个包含 1 到 n2 所有元素,且元素按顺时针顺序螺旋排列的 n x n 正方形矩阵 matrix 。
(EN)
Given a positive integer n, generate an n x n matrix filled with elements from 1 to n2 in spiral order.
Example 1:
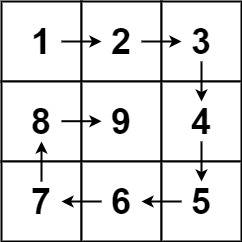
1 | Input: n = 3 |
Example 2:
1 | Input: n = 1 |
Constraints / 提示:
1 <= n <= 20
这道题本质上不涉及任何算法的,它主要考的就是一个过程的模拟。在二分法中,区间那块除了提到了左闭右闭区间,还提到了左闭右开区间,左闭右开区间针对多个连续的区间,最主要遵循的规则就是循环不变量规则,这回再把这个概念提出来,在解这道题的时候,也应把循环不变量用在过程模拟上面。
这循环不变量当中的 “量”,最主要指的就是判定规则作为循环遍历要保持一致,如果第一个区间规则是左闭右开 [l,r) ,那么后面的区间规则也应该是左闭右开,循环的规则要保持一致!
比如说这题,可以把正方形矩阵的四个角作为一个节点,如下图:
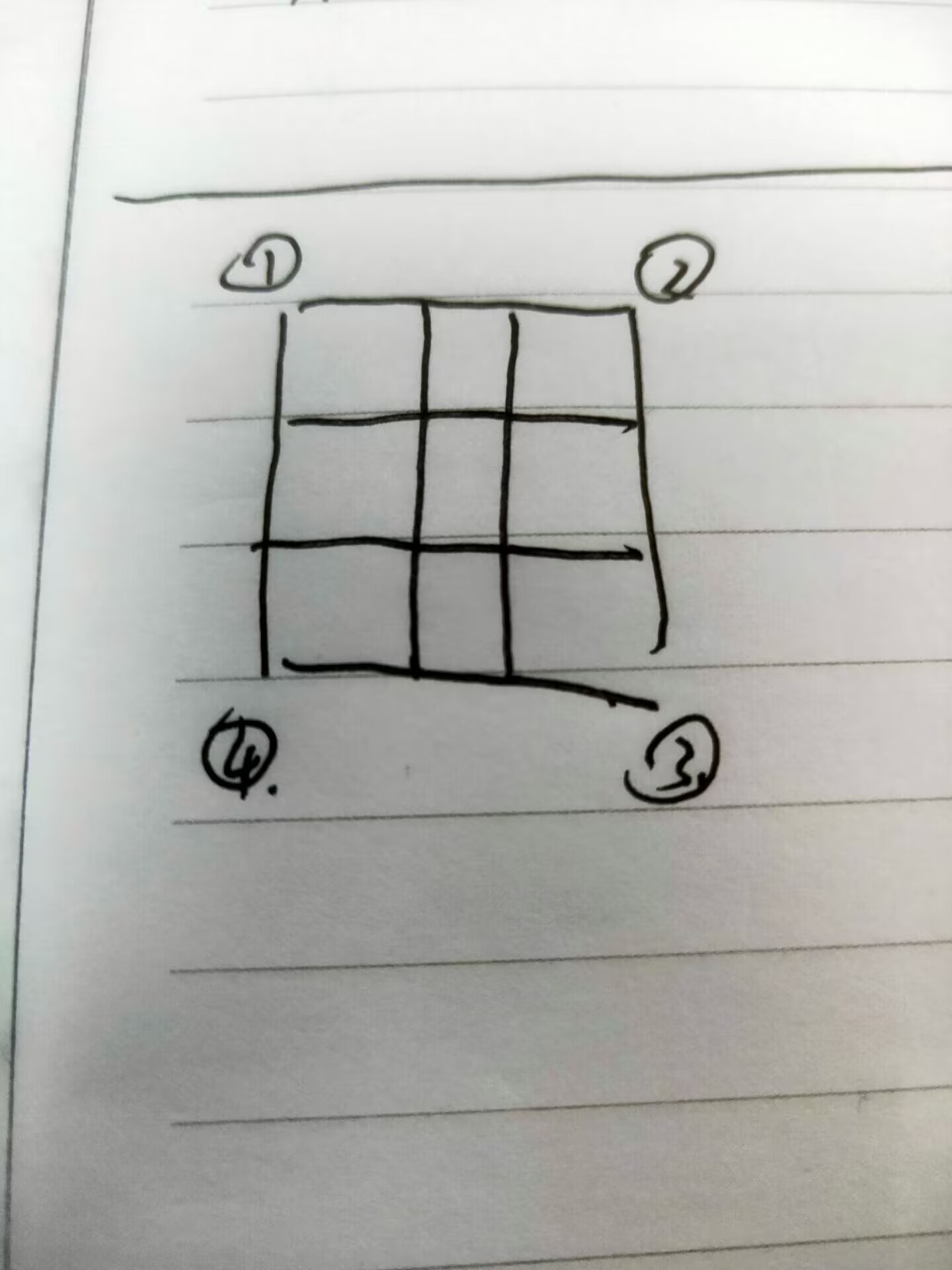
在循环遍历一圈时,如果区间是左闭右开,那么后面循环的区间也要左闭右开,也就是
1 | [1,2) |
这样我们保持一个区间,这样正方形矩阵的所有节点都能采到了。
这里有个非常容易搞错的点,就是在数学坐标轴中,向右则横坐标 x 递增;而在数组 [i][j] 中,顺时针遍历数组,却是 j 递增(在数组 [i][j] 中,i 实际上是数组的行,j 实际上是数组的列)。这是因为数组顺时针遍历时,会先遍历数组的列,行并没有发生变化。根据上述结论,设初始行位置为 starty ,初始列位置为 startx ,初始的遍历方向为顺时针方向,再定义一个初始位置为[starty][startx] , 这里以矩阵节点 1 所在的位置为原点为例,那么节点 1 的 startx = 0, starty = 0. 接着就可以得出:
从节点 1 遍历到节点 2 时,数组向右遍历,列发生变化,即 j++;又因为区间是左闭右开,在遍历时不应采上下一个节点。题目中的变量 n 其实就是 n.length (假设变量 n = 3, 数组的索引位置为 0,1,2,则在数组y中的最后一个位置就是 n.length - 1),那么再引入一个新变量叫 offset ,用来控制遍历时不会采到下一个节点。综上所述第一个(横向)遍历区间应该为:
1 | [starty, n.length-offset) |
也就是
1 | for (j = starty; j < n-offset; j++){} |
第二个遍历区间,只需把 starty 换成 startx 即可,同时要注意数组顺时针遍历时的行列变化。即:
1 | [startx, n.length-offset) -> |
接着第三个区间、第四个区间,同样要注意数组顺时针遍历时的行列变化,即
1 | [n.length-offset, starty)-> |
这时一圈的遍历就算结束了。接下来,要继续往里遍历,则初始位置和偏移值都要发生递增变化:
1 | startX++ |
这里又要分两种情况:
(1) 如果变量 n 为奇数,则不管转矩阵多少圈,最终都还剩中间一个没有遍历。所以应加一个判断
1 | if(奇数) -> 矩阵最中间的值计入计数,计数+1 |
(2) 如果变量 n 为偶数,则重复上述的遍历过程。
至此,矩阵的遍历就算全部结束了。重点还是要多多理解矩阵遍历的过程!
解法:
JavaScript:
(For Leetcode / WebStorm Custom)
1 | /** |
7. 59 题扩展题目
LeetCode 54. 螺旋矩阵 / Spiral Matrix
难度:中等
要求:
给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
(Given an m x n matrix, return all elements of the matrix in spiral order.)
Example 1:
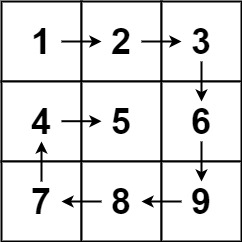
1 | Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] |
Example 2:

1 | Input: matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]] |
和 59 题不一样的是,这题输出的结果是遍历后的新数组,所以需要新创建一个数组用来存储遍历结果;数组不是单由变量 n 来创建的,而是由涉及行的变量 n 和涉及列的变量 m 来共同创建的。多了一个变量的影响,遍历圈数应该是由最大值的变量来决定而不是最小值的变量:(如图)
由于矩阵现在变为长方形,不加跳出条件很容易造成新数组的长度大于原数组的长度,所以在存储代码块处添加跳出条件,若存储的长度与原数组的长度完全相等时,直接返回新数组。
解法:
还是类似于模拟过程的解法。
JavaScript:
(For Leetcode / WebStorm Custom)
1 | /** |